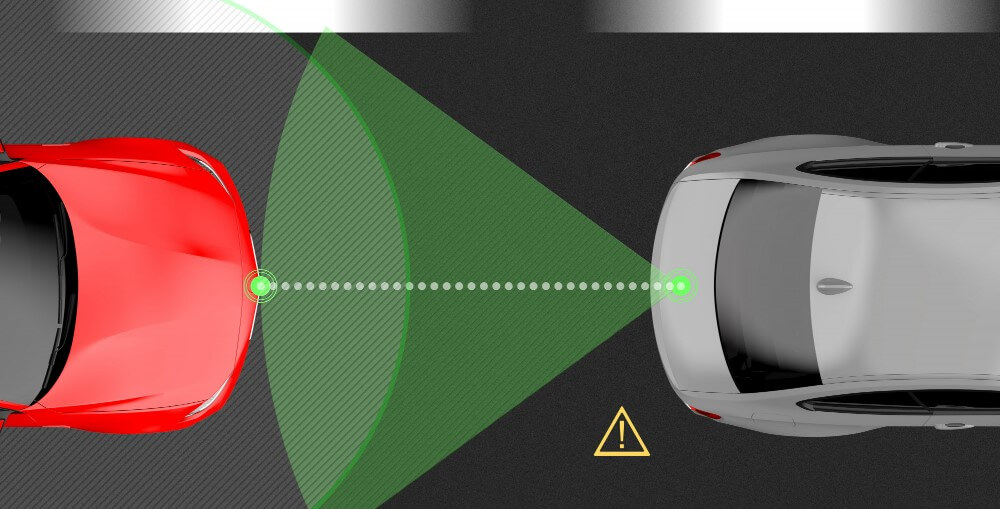
Lidar is a remote sensing technology that uses laser light to map the surface of the earth. Lidar mappers use this technology to create high-resolution maps of the earth’s surface. These maps can be used for a variety of purposes, including environmental monitoring, land use planning, and disaster response.

There are three primary types of LiDAR technology: airborne, terrestrial, and mobile.
Airborne LiDAR systems are mounted on aircraft and used to collect data over large areas.
Terrestrial LiDAR systems are mounted on tripods and used to collect data over smaller areas.
Mobile LiDAR systems are mounted on vehicles and used to collect data over medium-sized areas.
Map Generation using Lidar Mapper
Lidar is an acronym for Light Detection And Ranging. It is a remote sensing technology that uses laser light to map the surface of the earth. Lidar mappers are used to create high-resolution 3D maps of an area. Lidar mapping is a very accurate way to measure the elevation of an area.
It is often used in applications where a high degree of accuracy is required, such as in surveying and engineering. Lidar mappers work by sending out a laser beam and measuring the time it takes for the beam to bounce back. The mapper then uses this information to create a 3D map of the area.
Data Collection
Lidar mappers are a type of remote sensing equipment that utilizes laser pulses to collect data about an area. Lidar mappers can be used to create highly accurate three-dimensional models of an area, making them an invaluable tool for a variety of applications such as surveying, mapping, and land management. Lidar mappers work by sending out a laser pulse and measuring the time it takes for the pulse to bounce back off of objects in the area. By knowing the speed of light, the mapper can then calculate the distance to the object. Lidar mappers can also measure the intensity of the returned pulse, which can be used to create a three-dimensional model of the area.
Data Processing using Lidar Mapper
Lidar Mapper is a powerful data processing tool that can be used to create detailed 3D models of environments. It is often used in mapping applications, such as surveying land for development purposes. Lidar Mapper works by firing pulses of laser light at a target and measuring the time it takes for the light to reflect back. By measuring the distance between the laser and the target, Lidar Mapper can create a highly accurate 3D model of the environment. It is a valuable tool for many applications, including surveying, mapping, and land management. It can be used to create detailed 3D models of environments, which can be used to plan development projects or assess environmental.
Mapping
Lidar mapping is a remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to collect topographic data. Lidar can be used to create highly accurate and detailed digital models of the earth’s surface. Lidar mapping is often used in conjunction with other data sources, such as aerial photographs or GPS data, to create comprehensive maps. Lidar data can be used to create 3D models of the earth’s surface, as well as to measure the height, width, and depth of features. Lidar mapping is an increasingly popular tool for a variety of applications, such as surveying, engineering, environmental monitoring, and disaster response.
In conclusion, LiDAR is an optical remote sensing technology that bounces laser light off of the Earth’s surface and collects information about the Earth’s landscape. LiDAR systems send out pulses of laser light at varying levels of intensity. The reflected light is analysed and used to create a digital elevation model. LiDAR is typically mounted on vehicles, such as autonomous vehicles or airplanes. In 2018, there were 3.2 million LiDAR devices in operation and 2.8 million LiDAR systems in operation.
What type of data collection is LiDAR mapper?
LiDAR mappers collect data using laser scanning technology. This data is then used to create three-dimensional (3D) models of the mapped area. This type of mapping is ideal for large areas or areas with complex features.
What are the top 5 uses of LiDAR mapper?
The top 5 uses of LiDAR technology are:
1. To create highly accurate 3D maps of an area
2. To locate and identify objects in an area
3. To create virtual reality simulations
4. To detect land mines and other hidden objects
5. To study weather patterns and atmospheric conditions.
How do I get a LiDAR map?
If you’re looking to create a LiDAR map, there are a few things you’ll need to do. First, you’ll need to gather data from a LiDAR sensor. This data can be acquired through a variety of methods, such as using an airborne platform or a ground-based mobile mapping system. Once you have your data, you’ll need to process it using specialized software. This software will help you create a 3D point cloud, which is the basis for a LiDAR map. Once you have your point cloud, you can then create a map using a variety of mapping software packages.
What LiDAR does NASA use?
NASA uses LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) to measure distance by sending out short pulses of light and measuring how long it takes for the pulses to bounce back. LiDAR can be used to create 3D images of objects, and is often used for mapping and surveying purposes
How accurate is LiDAR mapping?
LiDAR technology has revolutionized mapping and surveying, providing accurate 3D data of any terrain. But how accurate is LiDAR mapping? Generally speaking, LiDAR mapping is extremely accurate. The margin of error is usually just a few centimetres. But there are factors that can affect the accuracy of LiDAR data, such as the density of vegetation, the angle of the LiDAR sensor, and the quality of the sensor itself.
That being said, LiDAR mapping is still the most accurate mapping technology available, and it will continue to be used for many years to come.
Does Google Earth have LiDAR data?
Google Earth does not currently have any LiDAR data available. However, there are a number of other ways to view LiDAR data, such as through the USGS National Map or the National Science and Technology Centre for Disaster Resilience.
How deep can LiDAR detect?
LiDAR can detect objects at a depth of up to 100m. However, the depth of detection may vary depending on the specific LiDAR system and the conditions under which it is used. For example, LiDAR may be less effective in detecting objects in murky water or in areas with dense vegetation.
What is the future of LiDAR?
The future of LiDAR technology is looking very promising. With the rapid advancement of laser and sensor technology, LiDAR is becoming more and more affordable and effective. The potential applications for LiDAR are endless, and the technology is constantly evolving. As LiDAR technology becomes more widely used, the price of LiDAR systems is expected to decrease. This will make LiDAR more accessible to a wider range of users, including small businesses and individual consumers. The accuracy and resolution of LiDAR systems are also expected to continue to improve. This will allow for even more precise measurements and analysis, making LiDAR an even more valuable tool for a variety of applications.