Fiber lasers are becoming increasingly important in technology, particularly in manufacturing. It provides a unique combination of high power and excellent beam quality, making them attractive for various laser processing applications. In this blog post, we will discuss the fundamentals of fiber lasers, including their types, applications, and more. We will explore the various advantages and disadvantages of fiber lasers compared to other laser technologies and discuss the potential for further advancements in the future. Additionally, we will look at some of the common safety considerations for using fiber lasers.
What are Fiber Lasers?
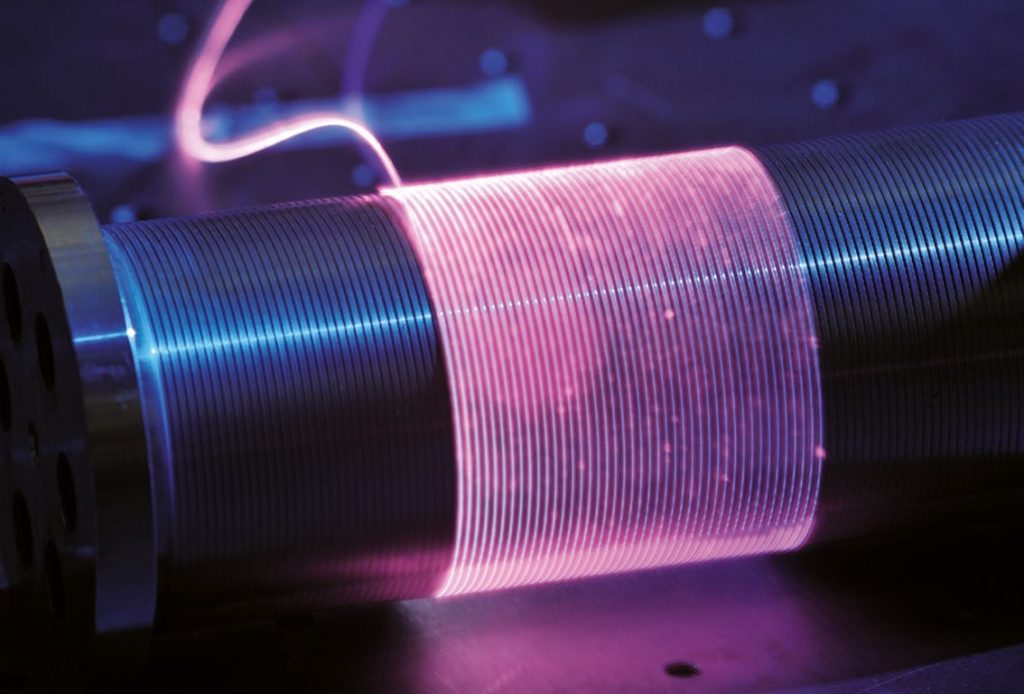
Fiber lasers represent a revolutionary advancement worldwide, providing an efficient and cost-effective way to produce high-quality laser light. A fiber laser is an optical fiber doped with rare-earth elements such as erbium, ytterbium, and thulium that emit laser light of different wavelengths. They are becoming increasingly popular in industrial applications, as they can achieve a wide range of tasks, such as cutting, welding, marking, engraving, and drilling.
Furthermore, they are highly efficient, with an extremely long lifespan, making them an attractive option for businesses looking to produce high-quality laser output. This blog post will discuss the basics of fiber laser technology and its many applications. Also, we will discuss how fiber lasers can be used in various industries. Finally, we’ll look at some of the challenges associated with that and how to address them.
How do Fiber Lasers Work?
Fiber lasers are named for their optical fiber active gain medium. Five main stages are involved in producing a well-collimated high-power laser from a fiber laser machine. The following are some of them:
- Pumping light into the system
- The optical fiber is collected and transported
- Optical fibers transmit pump light
- The laser cavity is stimulated to emit light
- Creating a laser beam from the raw laser light
Fiber Laser Applications
Fiber lasers are effective in many applications due to their wide power output range. Here are a few examples:
Laser Marking
As a general rule, 1064 nm ytterbium-doped fiber lasers are ideal for laser marking. With these lasers, you can mark plastic and metal with permanent, high-contrast marks. In addition to barcodes, logos, and other texts, OEMs and suppliers require laser marking machines.
Lasers can also be used for annealing, etching, engraving, and marking. There are both manual and automated versions of these machines.
Laser Cleaning
Laser cleaning effectively removes paint, oxide, rust, etc., from metal surfaces. The process can be automated and customized for different production lines.
Laser Welding
Fiber laser welding is another important application for these lasers. Due to the variety of benefits offered by fiber laser welding, it is gaining market share fast. Laser welding offers faster speeds, greater precision, lower deformation, and better quality than traditional welding methods.
Laser Cutting
The use of fiber lasers for laser cutting has been extensively researched. Its edge quality is impressive, making it ideal for parts with close tolerances. As a result of its long list of benefits, fabricators are adopting it across the board. In the next section, we will examine what these benefits are.
Fiber Laser Cutting Benefits
A fiber laser has several features that make it more suitable for widespread commercial use than other laser types. These are divided into four categories:
Fiber Laser Process Benefits
- Stability is increased
- Efficiency at its best
- High-quality beams
- A simple integration process
- The process was conducted without contact
Cost Benefits of Fiber Laser
- Long-term cost-effectiveness
- High energy efficiency (75%, compared to 20% for CO2 lasers)
- Waste reduction
- Power consumption is reduced
- Redundancy of operators is reduced
- Operational costs are low
Equipment Benefits
- A wide range of applications
- Smaller footprint and more compact
- Effortless maintenance
- No periodic re-alignment of mirrors required
- Reduction in set-up and downtime
- Eliminated tooling charges
How does A fiber laser cut metal?
A fiber laser cuts metal using a highly focused laser beam to heat, melt, and vaporize the metal material. The laser beam is generated by a fiber laser source and transmitted through lenses and mirrors to the cutting head. This cutting head is typically mounted on a gantry and is moved over the surface of the metal to be cut. The laser beam is focused onto a small spot on the metal surface, usually about 0.2 mm in diameter.
The heat generated by this focused beam melts the metal in the area of the spot, and then a high-pressure gas, such as nitrogen or oxygen, is used to blow away the molten metal, creating a cut in the metal. Multiple laser passes may be necessary to create a complete cut depending on the material and its thickness. The process of laser cutting metal can be done with various laser sources, including CO2 and excimer lasers.
In conclusion, fiber lasers have revolutionized the industry and quickly become the go-to laser type for many applications. They are becoming increasingly efficient and cost-effective and are used in various industrial and medical applications. As technology develops, fiber lasers will become an even more useful and important part of our lives.