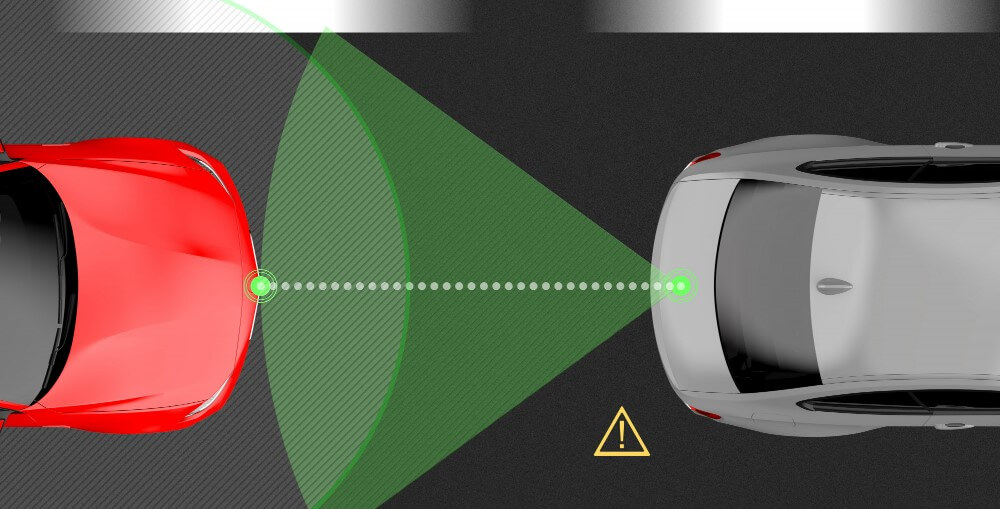
Artificial Intelligence is being made possible in several domains thanks in large part to sensor-based technology. One of the most exciting sensor-based technologies utilized is LiDAR sensors in autonomous vehicles. Such autonomous vehicles have to become aware of their surroundings and travel safely without any chance of collision.
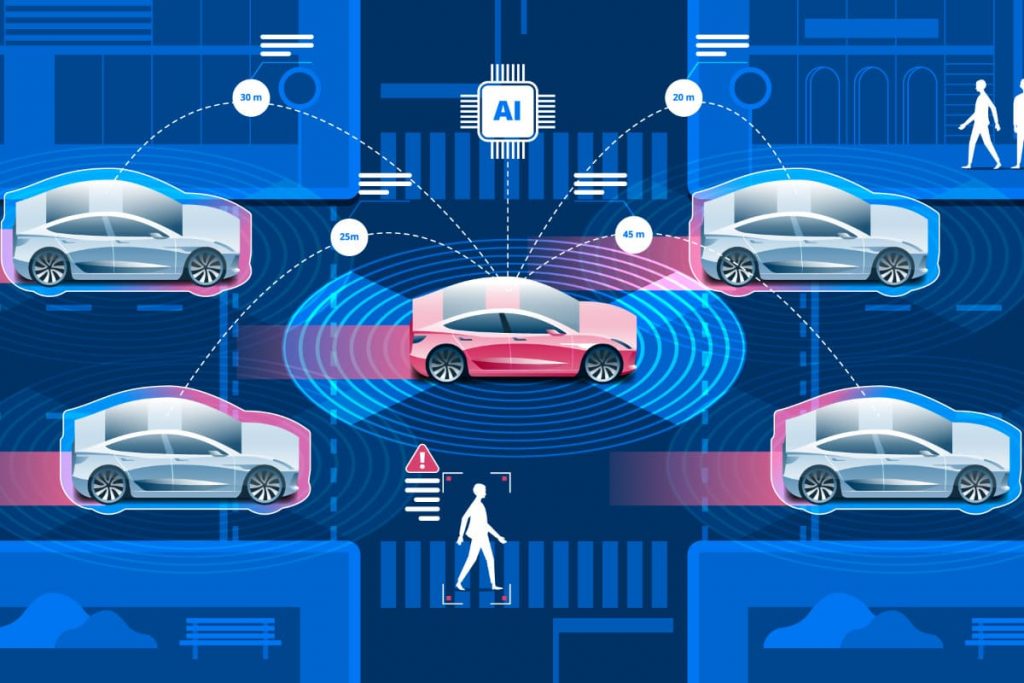
LiDAR sensors in autonomous vehicles help the vehicles recognize objects in-depth. We will now talk about how LiDAR sensors in autonomous vehicles work, and why it is important for autonomous or self-driving vehicles.
How Do LiDAR Sensors In Autonomous Vehicles Work?
When viewed from a distance, LIDAR performs very similarly to sonar systems, which produce sound waves that are directed in all directions until they come into touch with an object, at which point they resonate and return to their source. Then, using the time it took for the echo to return and the established speed of sound, the distance to that item is computed.
The speed of light, which is more than 1,000,000 times faster than the speed of sound, also applies to how LiDAR systems work. They thereby transmit and receive data from hundreds of thousands of laser pulses every second rather than creating sound waves. Each laser’s reflection point is recorded by an onboard computer, and this quickly updating “point cloud” is then transformed into an animated 3D depiction of the environment.
The scanner, laser, and GPS receiver are the three primary parts of a LiDAR device. Adding to the list of essential parts for data collection and processing are the photodetector and optics. Nowadays, the majority of public and private entities collect LiDAR data using airplanes, autonomous aircraft, and helicopters.
Use Of LIDAR Sensors In Autonomous Vehicles
Radar has long been used in the vehicle industry to automatically regulate speed, brakes, and safety systems in reaction to abrupt changes in traffic circumstances. LIDAR is now being included by automakers in ADAS to help drivers better understand the dynamic settings in which their vehicles operate.
Using a variety of valuable statistics from the integration of automotive platforms, ADAS systems are able to perform hundreds of precisely calculated driving decisions every minute. We recognize this technology as a crucial element in creating new driver-aid features that can direct the development of fully autonomous self-driving automobiles with safe and secure travel.
How LiDAR Sensors In Autonomous Vehicles Are Making Self-driving Safer?
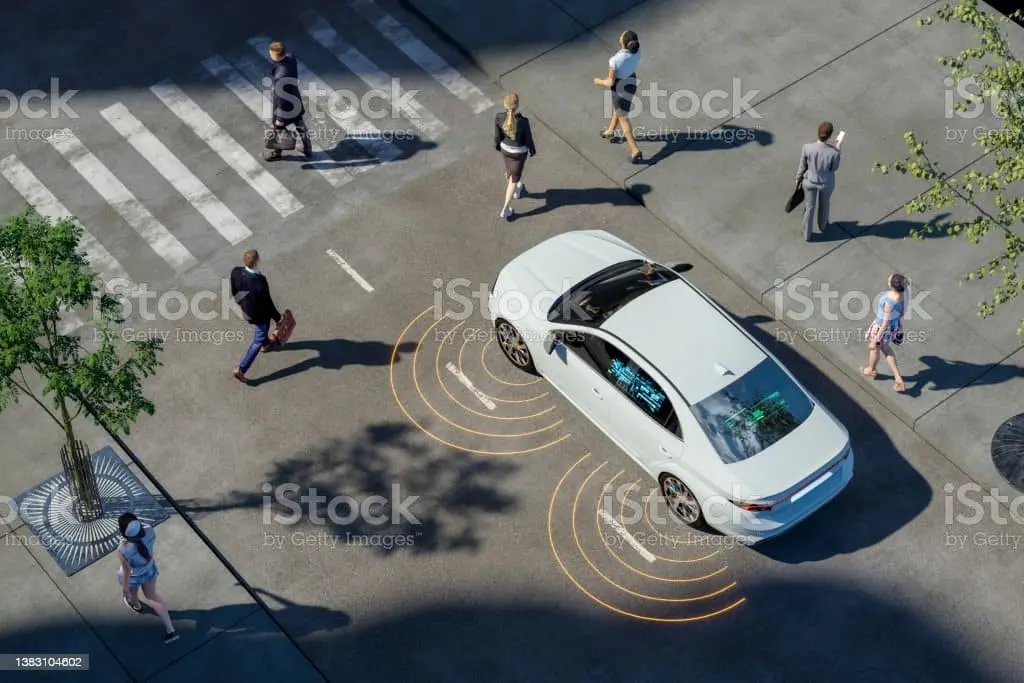
As is well known, LiDAR is a radar-like detection system that detects objects, describes their characteristics and determines their distance by using light waves rather than radio waves. In addition to detecting the movement and velocity of nearby objects, cars, their own motion in relation to the ground, and several other items, Lidar goes a step further.
To enable the transition from driver assistance to fully autonomous vehicles, LiDAR-based 3D sensing is thus a crucially important technology. LiDAR sensors in autonomous vehicles assist in gathering crucial information about the environment’s surroundings that ADAS needs to provide trustworthy safety.
ADAS will depend more and more on LiDAR to improve perception capabilities in all kinds of operating settings as vehicles grow more autonomous and take over the primary extra driving responsibilities.
Why LiDAR Sensors In Autonomous Vehicles Are Important?
A self-driving car cannot function without a precise and quick object-detecting system. With a continuously spinning LiDAR system that emits millions of laser pulses every second, LiDAR makes this possible. These pulses hit the nearby objects and reflect back.
Furthermore, a 3D point cloud is produced using these light reflections. In order to make such items recognizable to autonomous vehicles through LiDAR sensors, an onboard computer records each laser’s reflection point and converts this quickly updated point cloud into an animated 3D representation formed by 3D point cloud annotation.
LIDAR Annotation 3D Point Cloud Labeling Service
It is crucial to feed the AI model a massive volume of annotated photos produced by the LiDAR sensors in order to train it to detect or distinguish objects using the LiDAR sensors. The most accurate method for categorizing things with the additional property that a perception model can notice for learning is LIDAR point cloud segmentation.
The data annotation for LiDAR enables more accurate lane detection and multi-frame tracking of the object, which aids self-driving cars in comprehending their surroundings. The best feature of LiDAR is cloud annotation, which allows objects up to 1 cm in diameter to be marked up with 3D boxes at each point.