It has been a while since Sensor Lidar made headlines. It promises to revolutionize transportation. With its precise 3D mapping capabilities and advanced obstacle detection, it is set to play a critical role in making self-driving cars a reality. In this article, we dive into the workings of Sensor Lidar, exploring its benefits and limitations and uncovering the key factors that make it a game-changer in the world of autonomous driving.
Unlock the mysteries of Lidar technology and discover the future of autonomous driving! Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or simply curious about the future of transportation, this is the article for you!
What is Sensor Lidar?
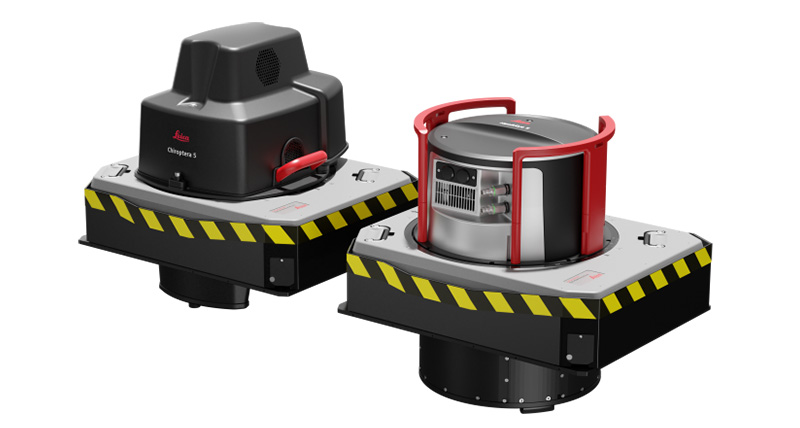
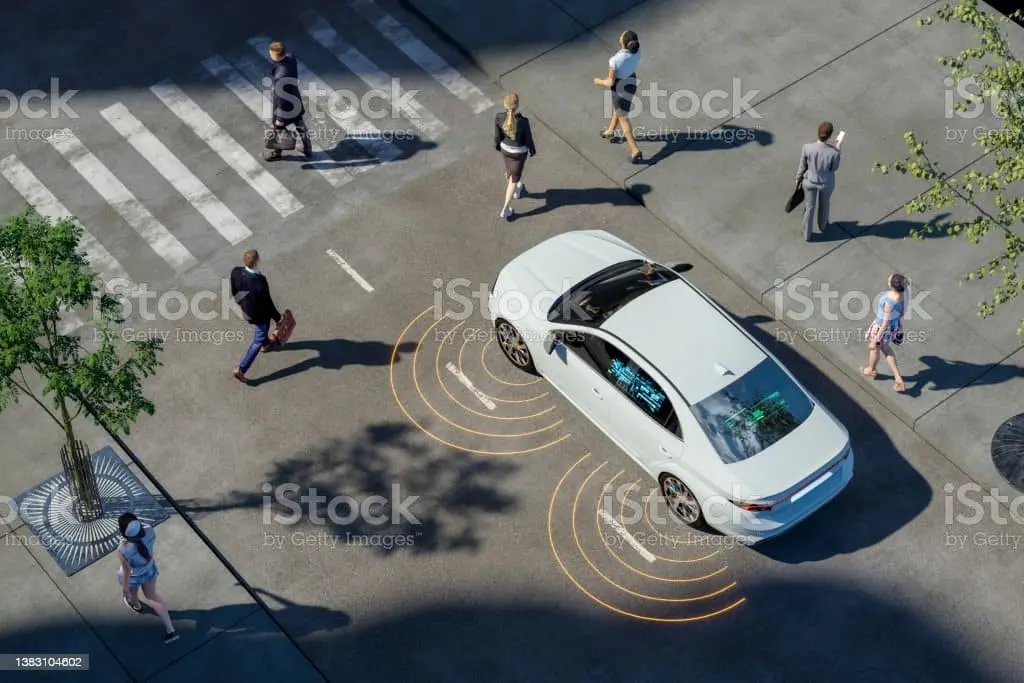
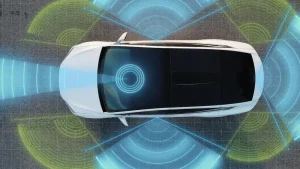
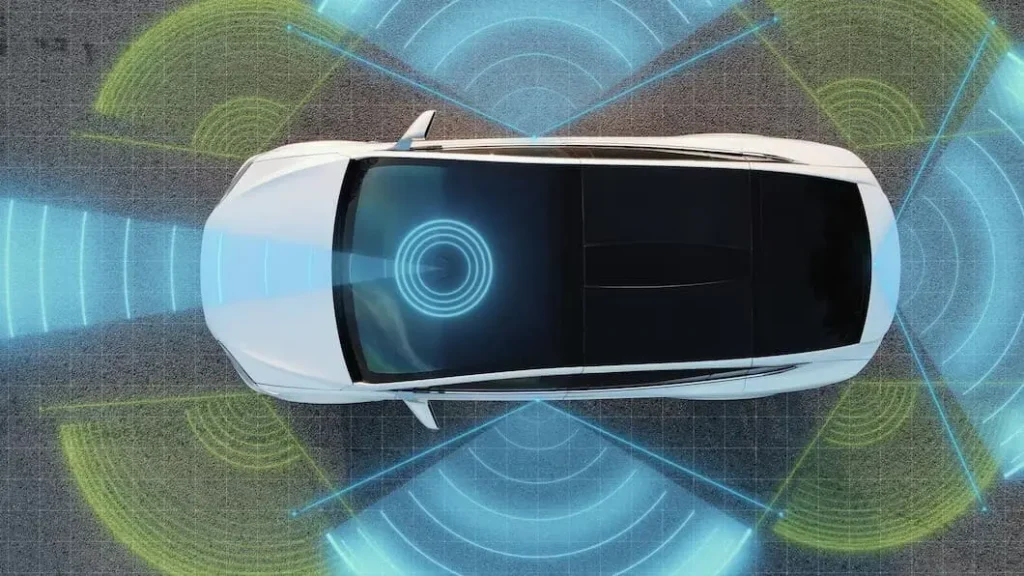
Light Detection and Ranging (Lidar) creates 3D maps using laser light sensors to detect and track objects in the environment. It measures the time it takes for the reflected light to return to the sensor after emitting a laser beam, allowing it to locate objects based on their distance. As a result, this information is combined with data from other sensors. As a result, it provides precise and real-time information about the environment. There are many applications for sensor Lidar, including autonomous vehicles, robotics, and surveying.
How does Sensor Lidar Work?
It works by emitting a laser beam and measuring the time it takes for the reflected light to return. In Lidar, a laser beam bounces off objects and returns to the sensor, measuring the time it takes the light to travel to an object and back. This way, the Lidar sensor can create a 3D map of the environment thousands of times per second. When the sensor knows the speed of light and how long it takes to return, it can figure out how far an object is.
A real-time environment map is then created by the Lidar’s onboard computer, using algorithms to interpret the data. This map is used by autonomous vehicles and other applications to navigate their surroundings, detect obstacles, and make decisions about their actions.
Applications of Sensor Lidar
Lidar Sensor is used in a wide range of fields, including:
Autonomous Vehicles
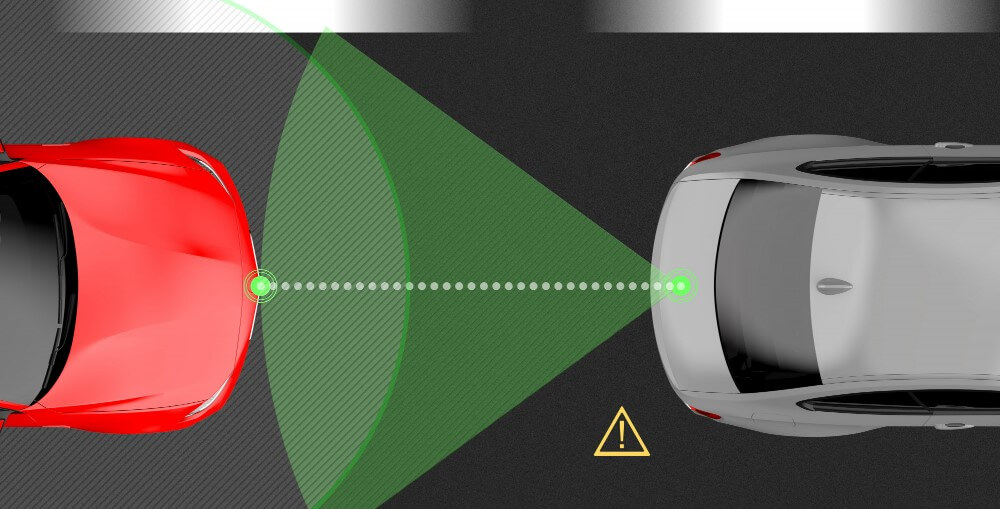
It is common for autonomous vehicles to use the Lidar sensor to provide real-time information about their environment. A vehicle uses Sensor Lidar data to navigate, avoid obstacles, and decide what to do.
Robotics
As part of robotics applications, sensors Lidar provide real-time data about the environment. Robots use this data to guide their movements, avoid obstacles, and interact with the environment.
Mapping
It is widely used in mapping applications to create detailed 3D maps of the environment. The data collected by Lidar Sensor is used to create maps of forests, cities, and other areas, providing information about the shape and location of objects in the environment.
Advantages of Sensor Lidar
It is advantageous to use Sensor Lidar for several reasons, including:
Real-time Data Collection
It provides real-time data about the environment, allowing for quick and accurate navigation and decision-making.
Detailed 3D Maps
An object’s shape and location in the environment are captured in 3D maps.
High Precision
It is highly precise, providing accurate measurements of distances and locations.
Disadvantages of Sensor Lidar
Additionally, there are several disadvantages to using Sensor Lidar:
Cost
The cost of Lidar Sensor technology makes it difficult for some applications to adopt it.
Weather Dependence
This technology is weather-dependent, and fog and rain can affect its performance.
Power Consumption
Lidar sensors require a lot of power, which can be challenging in some applications.
Conclusion
We are changing how we interact with our surroundings with the help of Lidar Sensor. It will be crucial to developing autonomous vehicles, robotics, and other cutting-edge applications thanks to its 3D mapping abilities and automated obstacle detection. It’s essential to understand how Sensor Lidar works if you want to appreciate its full potential, whether you’re a tech enthusiast or simply interested in the future of transportation.