3D lidar technology is a remote sensing technology for measuring distances in an environment using light detection and ranging, also known as LiDAR.
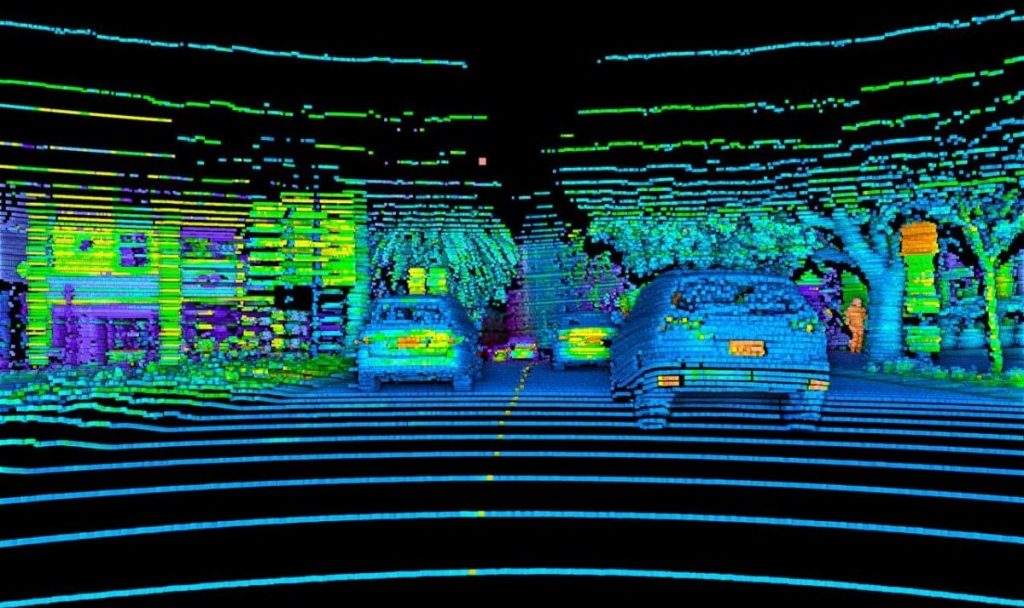
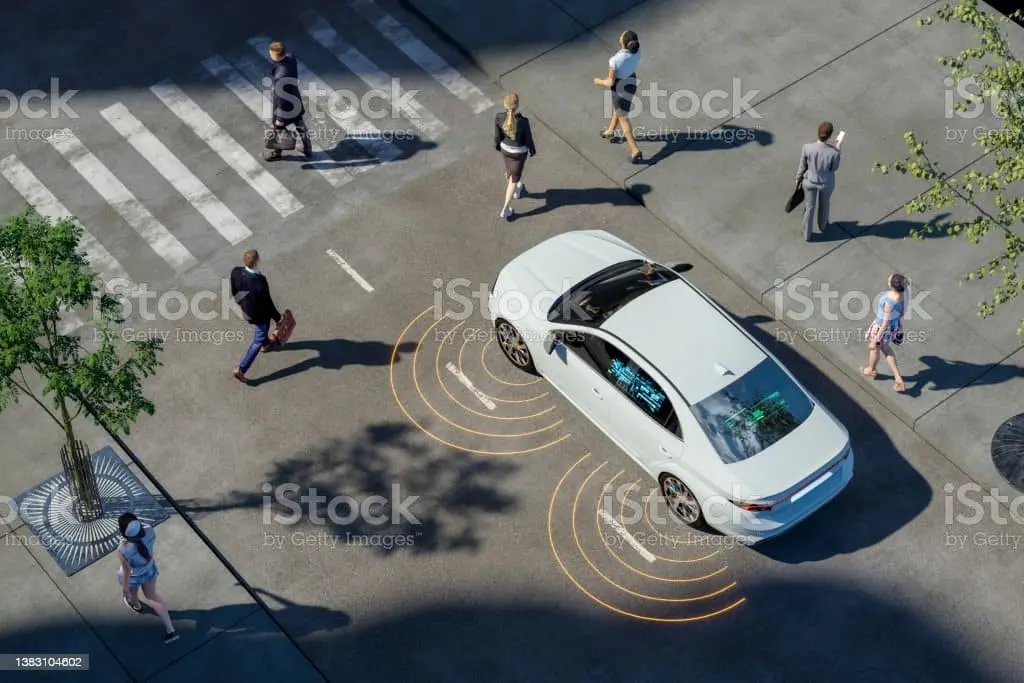
It plays a key role in embedded vision systems’ success. This leads to more advanced technologies emerging all the time, such as Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR). They have become increasingly important in areas like autonomous vehicles, factory automation, and smart retail.
The earliest method of 3D depth sensing uses passive stereo cameras to calculate the disparity of pixels from two in-sync sensors. In contrast, passive technology does not work in the dark. Furthermore, the texture of objects in the scene affects the depth quality. In order to overcome this problem, active stereo vision technology is used.
Read Also: How Do Marine LiDAR And Bathymetric Work Underwater?
3D LiDAR technology can be divided into two types.
Based on their functions, 3D LiDAR systems can be divided into Airborne LiDARs and Terrestrial LiDARs.
Airborne LiDAR
It is common for 3D lidar sensors to be mounted on aircraft such as drones and helicopters. Light pulses are sent toward the ground surface, where they are returned immediately after hitting an object to provide the exact distance. In addition to topological LiDAR, it can also be categorized into bathymetric LiDAR, which uses water-penetrating green light to measure seafloor and riverbed elevations.
Terrestrial LiDAR
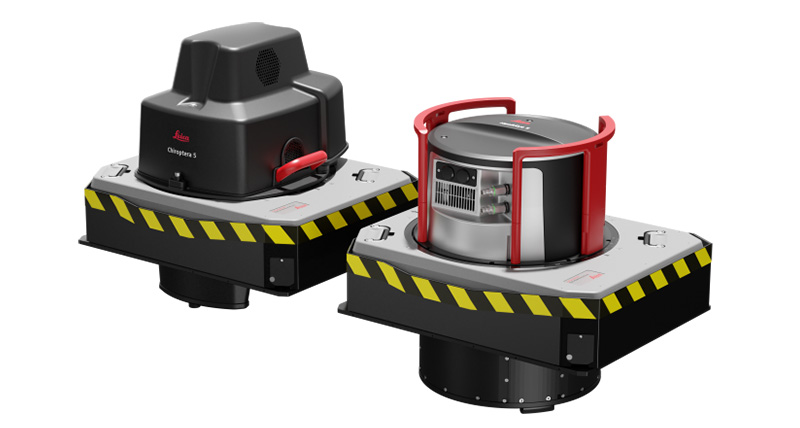
Terrain LiDAR systems are mounted on moving vehicles or tripods. 3D lidar sensors are used to map the natural features of buildings and to observe highways in high detail. The tool can also be used to create accurate 3D models of heritage sites. There are two types of terrestrial LiDAR systems: mobile and static.
What is the process of LiDAR?
In order to measure distance accurately with light, 3D LiDAR technology was developed.
Lidar uses laser pulses, which are sent from a transmitter and reflected from objects in the scene in 3D.
Since light travels at a constant speed, the system receiver detects reflected pulses. LiDAR’s point clouds, which capture instantaneous data, are called a “frame.”
With 3D LiDAR technology, you can measure distances to almost anything, including terrain, vegetation, buildings, vehicles, and people.
What is the source of LiDAR?
The LiDAR technology is an old one, but it has been rebranded and developed for various applications. LiDAR uses light to measure distance.
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) is a short-range radar system that was used in the 1950s to measure distances to buildings, trees, and other obstructions.
Read this: How 3D Laser Scanning Services work For Architecture And Construction business.
We now know this scanning technique as LiDAR. As early as the 1970s, scientists began experimenting with LiDAR for measuring distances to the surface of the earth. The Apollo 15 astronauts used LiDAR to map the moon’s surface in 1971. As LiDAR sensors became more popular in the 1990s and 2000s, digital elevation models and maps of terrain began to be created.
Since ancient times, it has been used to survey land in areas such as construction, forestry management, and mineral exploration.
Final Thoughts
A LiDAR device uses light to illuminate a target and measures reflected pulses from that target for estimating the distance to that target.
In the early 1970s, LiDAR was used to measure and map the earth’s surface; today, it’s being adapted for many different market applications. Although it is still challenging to integrate due to a lack of standardization between manufacturers, high processing demands, and overall complexity.
Read this: What is A Car Proximity Sensor And How Do They Work?
Now that Outsight’s 3D preprocessing software is available, these challenges can soon be overcome.