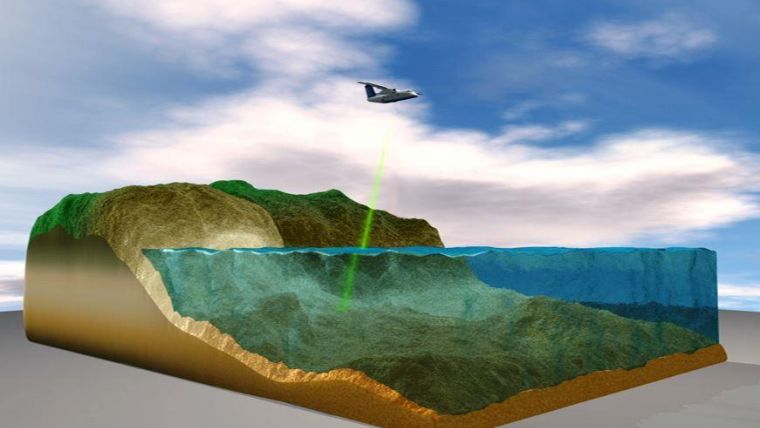
The Greek words “bathus,” which means “deep,” and “metron,” which means “measure,” are combined to form the English word “bathymetric.” Therefore, bathymetric Lidar is used to measure the depth of huge bodies of water, such as lakes and ocean floors. This procedure was carried out using different methods prior to the development of the new technology in bathymetric lidar for analyzing the floors of enormous water masses. These precautions involved the use of a hefty rope that was pre-measured or any other material that resembled a rope. The material could be lowered from the ship’s side, but this method was inefficient and inaccurate, necessitating the development of alternate methods.
What is today’s method of Bathymetric Lidar?
Today, sonar mounted beneath or even over the side of a water vessel, such as a boat, provides the data necessary to create bathymetric maps. The time it takes for a sound beam to descend to the ocean floor or from the Lidar systems provides information about the depth of the sea, ocean, or even a lake. The time it takes for light or sound to travel through the water, bounce off the seafloor, and return to the sounder is what determines how far away the seafloor, ocean bottom, or any other big body of water is.
A look at the history of Bathymetric
By the 1930s, single-beam sounders were used to create bathymetric maps. Multi-beam echo sounders are a tool used by experts in this sector, and modern technology has greatly advanced it. This method makes use of numerous closely spaced thin beams that are positioned in a manner that resembles a fan swath. This array of small individual beams is closely packed with these beams to offer excellent accuracy and angular precision. It is clear that a boat can survey more seafloors quickly with a depth-dependent wide swath than with a single beam echosounder since it requires fewer passes.
Depending on the depth of the water body being worked on, the beams are capable of updating anywhere between 0.1 and 50 Hz numerous times per second. This relates to boat speed while there is complete seafloor coverage.
Uses of Bathymetric Lidar
Remote sensing of coastlines is carried out using bathymetric Lidar.
It’s all about monitoring, detecting, and detecting. Even while it can be done in other regions of the world in a manner similar to this, this practice only applies to the American system. For coastal demarcation, visual interpretation of data from aerial remote sensing is well-known and frequently used. For monitoring, extracting, and detecting coastal lines, a variety of methods and remote sensing data are available.
It is employed in both the study of historical landscapes and archaeological research.
This makes use of remote sensing technology. The application of bathymetric lidar in these areas has transformed archaeology. Researchers in landscape archaeology, often known as the field of settlement, have taken an interest in light detection and ranging (LiDAR), a remote sensing technique that uses lasers as topographic scanners capable of piercing foliage. This technology allows for the display of the same landscapes in ways that were before impractical while also providing extensive data on the terrain for enormous spatial expanses. The data and visualizations have both been utilized to gain a better understanding of historical landscapes and how older people used them in the past.
Measuring breaking waves.
Another area where bathymetrical Lidar is used is in this one. Many processes, including bedform and beach erosion, are thought to be brought on by the waves’ energetic breaking. Other natural processes, such as currents, tides, winds, and river runoffs, among others, may also be to blame. In response to breaking waves, the profile shape creation on beaches emerges. LIDAR is utilized to keep an eye on the shoreline. The beam signals reflected by breaking and broken waves within the coast can also be detected by the terrestrial LIDAR.
Exploration of Spatial and Temporal Trends in Commercial Fishing uses bathymetric Lidar.
The fact that fishing is a food-producing activity and a major source of income for the diverse world’s population makes it crucial to preserve this limited resource. In order to provide information regarding the spatial and temporal footprint of fisheries, bathymetrical Lidar is used. This method is employed to keep track of fishing vessels in a variety of fishing operations. This is crucial for evaluating fishing activities and providing the marine spatial with data for accurate planning.
Conclusion
Bathymetric Lidar has proven to be quite useful for exploring other areas and analyzing the bottoms of big bodies of water. With the aid of technology, man has been able to do excellent research in fields where no one would have believed it was possible.